Input on AWS-driven form field part 2
- Troy Dieter
- Aws
- December 20, 2023
Table Of Contents
Advanced form-field solution architecture hosted by AWS (v2) - newly revised based on input!
Hi #AWS builders - I really appreciate the input from the community on the initial design! I’ve revised the architecture based on community recommendations:
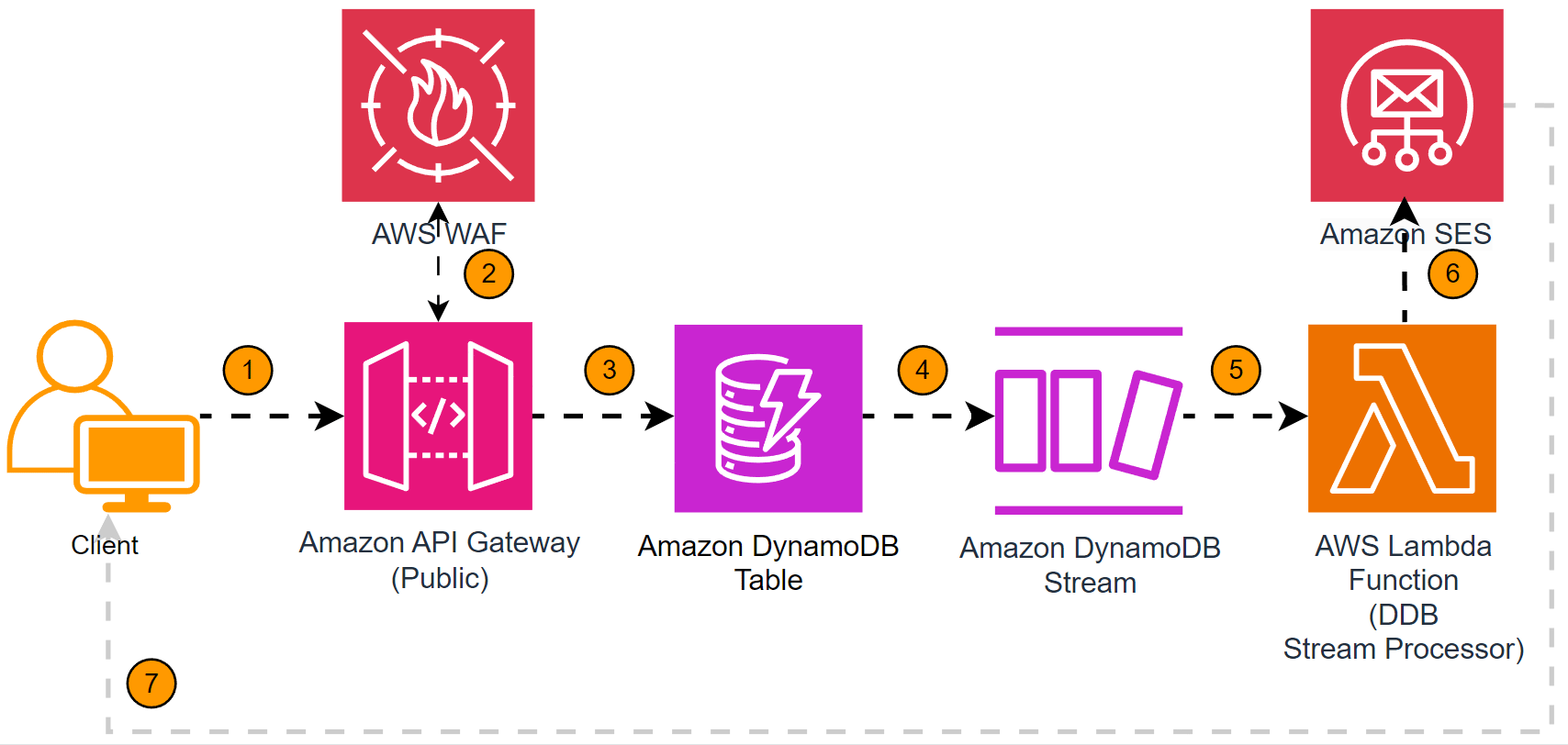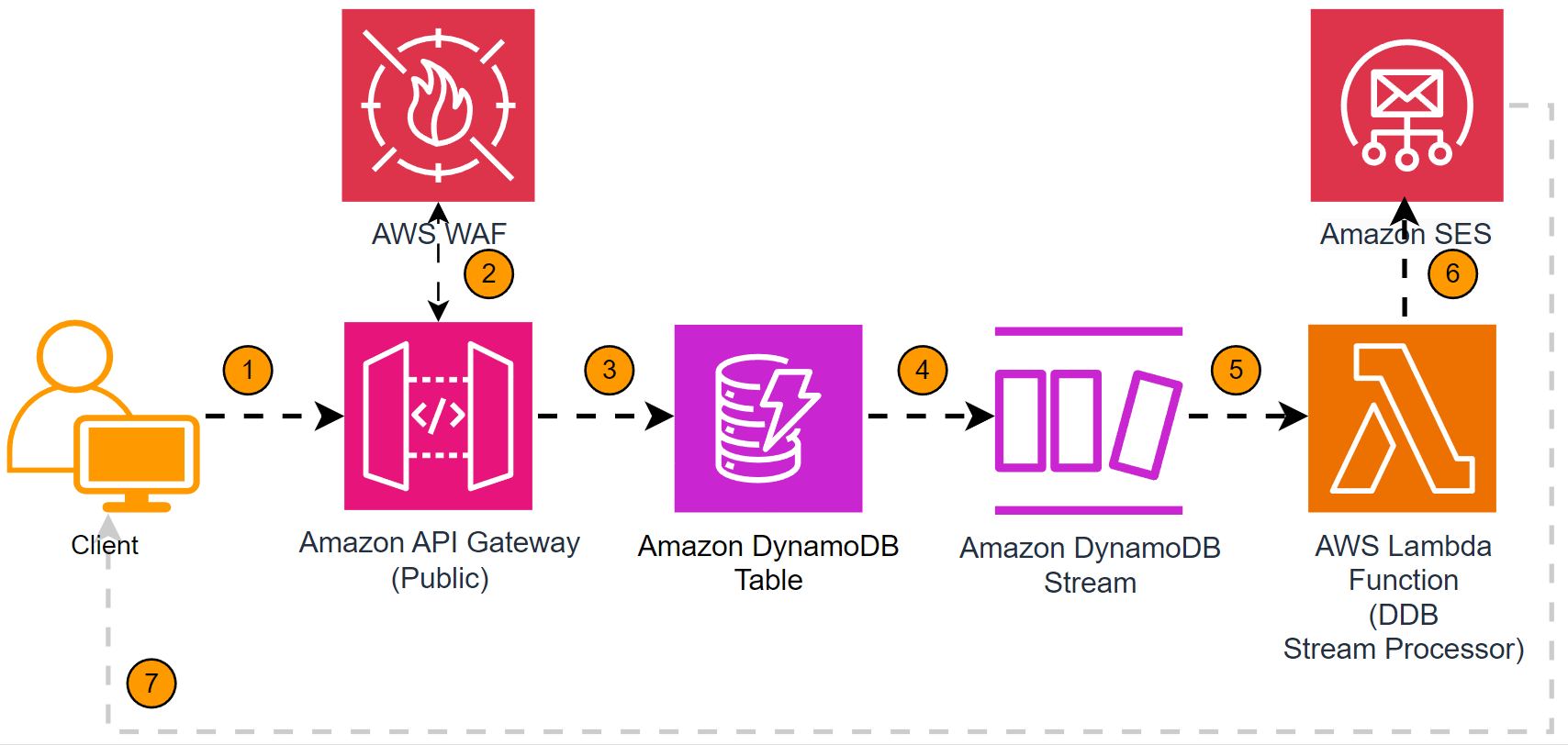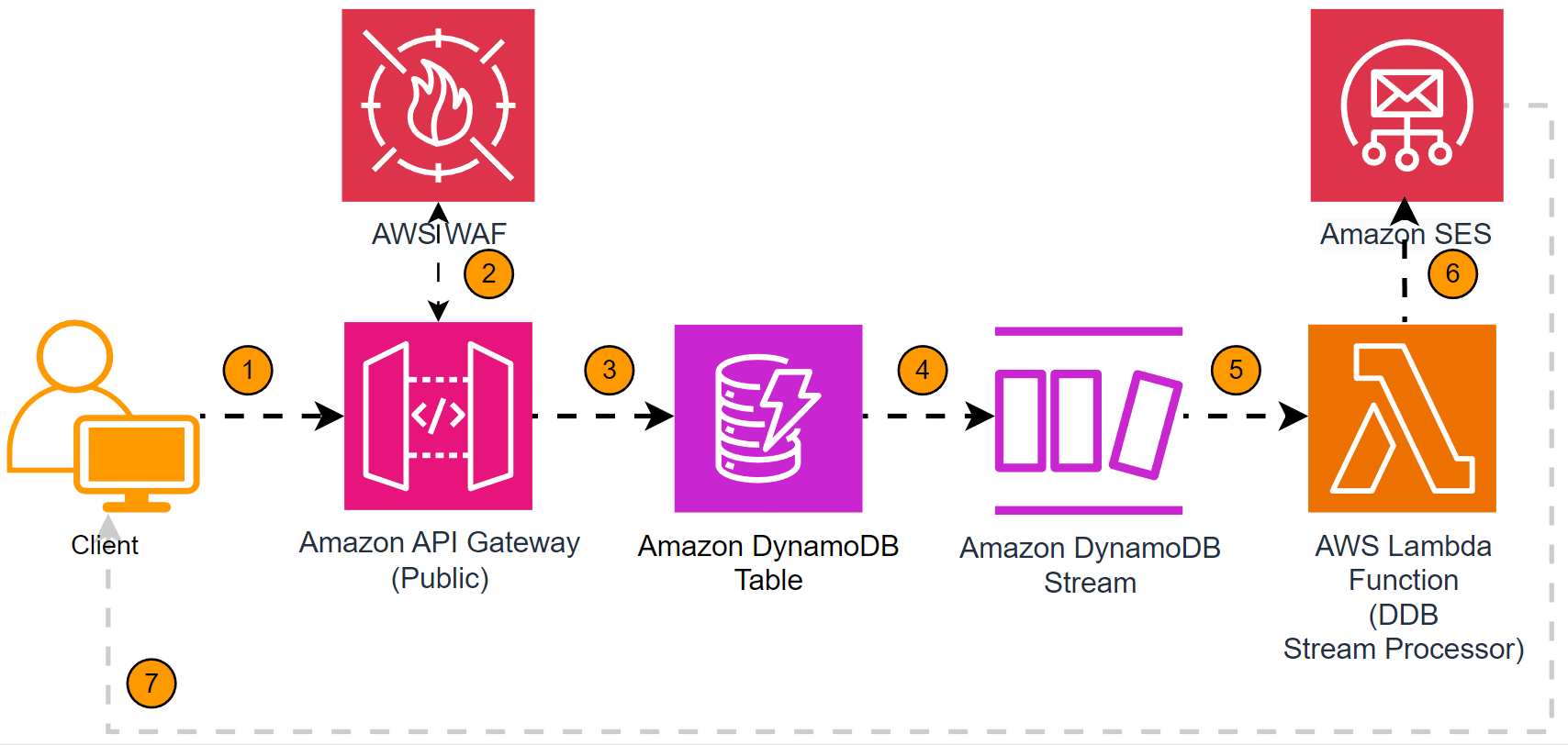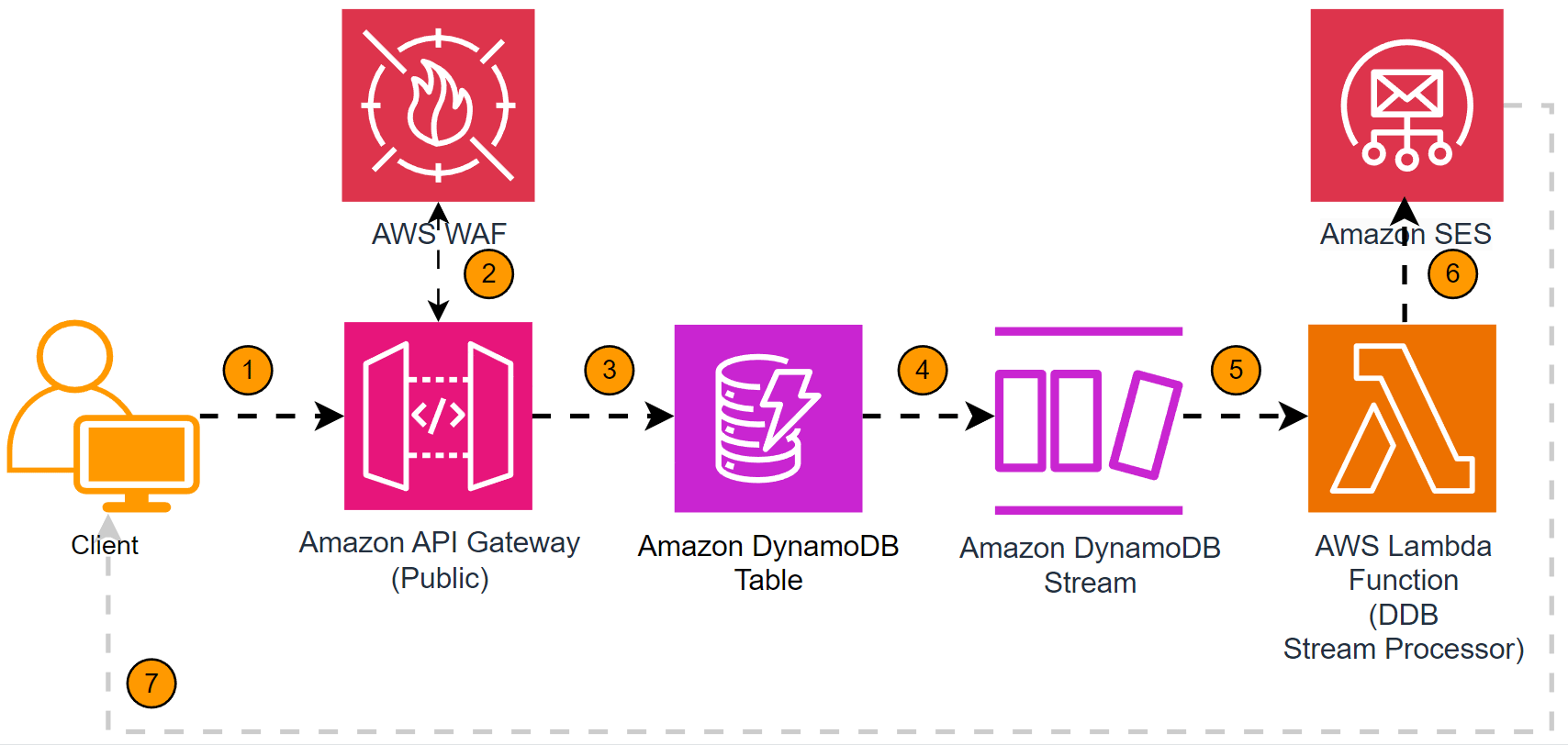
Client enters the site, enters their email to be informed of upcoming events, etc. This is a SPA (single-page application) hosted by Amazon CloudFront, serving Amazon S3 as the origin. A CAPTCHA is used to prevent spam/etc.
- The
onClickevent on the form execute’s POST to the API endpoint hosted within the API Gateway endpoint as defined in step - Once validated (
API Key), the event payload is sent to the queue. CORS ensures it’s being submitted through the originating site.
- The
AWS WAF evaluates it via the corresponding AWS WAF rule (
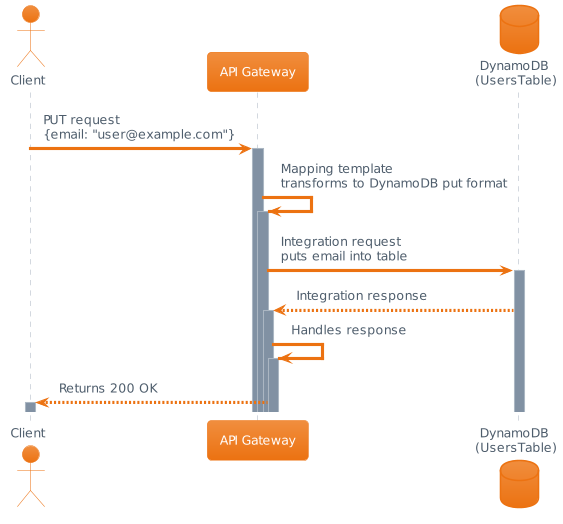
AWSManagedRulesCommonRuleSet) - noted here. This will help to preventCrossSiteScriptingattacks and the similar.Utilizing a mapping template, Amazon API Gateway is able to translate the request into something DynamoDB can receive securely and in its native input language. Here’s a breakdown:
- Client sends API Gateway a PUT request with the email
- Mapping template transforms this into DynamoDB put format
- Integration request puts the email into the DynamoDB table
- Gets integration response from DynamoDB
- Returns 200 OK response to client
To further describe, a simple userflow:
We then enable DynamoDB Streams and add an
event source mappingfor an Amazon Lambda function to receive these events. Here’s a breakdown:- When an item is inserted/updated in the DynamoDB table, a record is added to the DynamoDB Stream
- The stream buffers the inserts/updates (24 hours by default)
The associated Lambda function receives events from the stream and processes them.
- The Lambda function processor is triggered when stream records are available
- Lambda process the event record, performs any needed transformations
The Lambda function reads the event from the stream and send it to Amazon SES for processing.
Amazon SES ships the email from noreply@xyz.com from the trusted domain with the necessary details.
I’m looking forward to sharing the code for this once it’s completed! Stay tuned! :)


